One of the greatest advantages of 13 C-NMR compared to 1 H-NMR is the breadth of the spectrum – recall that carbons resonate from 0-220 ppm relative to the TMS standard, as opposed to only 0-12 ppm for protons. Because of this, 13 C signals rarely overlap, and we can almost always distinguish separate peaks for each carbon, even in a relatively large compound containing carbons in very similar.. 13.10 • 13 C NMR Spectroscopy: Signal Averaging and FT-NMR In some ways, it’s surprising that carbon NMR is even possible. After all, 12 C, the most abundant carbon isotope, has no nuclear spin and can’t be seen by NMR. Carbon-13 is the only naturally occurring carbon isotope with a nuclear spin, but its natural abundance is only 1.1%.

1H and 13C NMR Chemical Shifts of Pd(II) and Pt(II) Compounds z H NMR

Expanded carbonyl carbon region of the 13 CNMR spectrum of the P

13c Nmr Cheat Sheet

Organics Free FullText 13C NMR Spectroscopic Studies of Intra and
Carbon13 NMR Structure Determination of Organic Compounds Organic

13 C NMR chemical shifts of the carbonyl carbons of… Download

organic chemistry Assigning carbon13 NMR for ethyl 2oxo2Hchromen3
13.10 Characteristics of ¹³C NMR Spectroscopy Chemistry LibreTexts
13.11 Chemical Shifts and Interpreting ¹³C NMR Spectra Chemistry

Proton NMR 5 Carbonyl Compounds YouTube

13 C NMR chemical shifts of the carbonyl carbons of… Download

13C Carbon NMR Spectroscopy Chemistry Steps

13 C NMR chemical shifts of the carbonyl carbons of NBocLalanineOMe
The 13 C NMR Spectra of the Quaternary Carbon Resonances of TMP for a
The basics of 13CNMR spectroscopy

1 H and 13 C NMR spectrum of AMPDB. Download Scientific Diagram
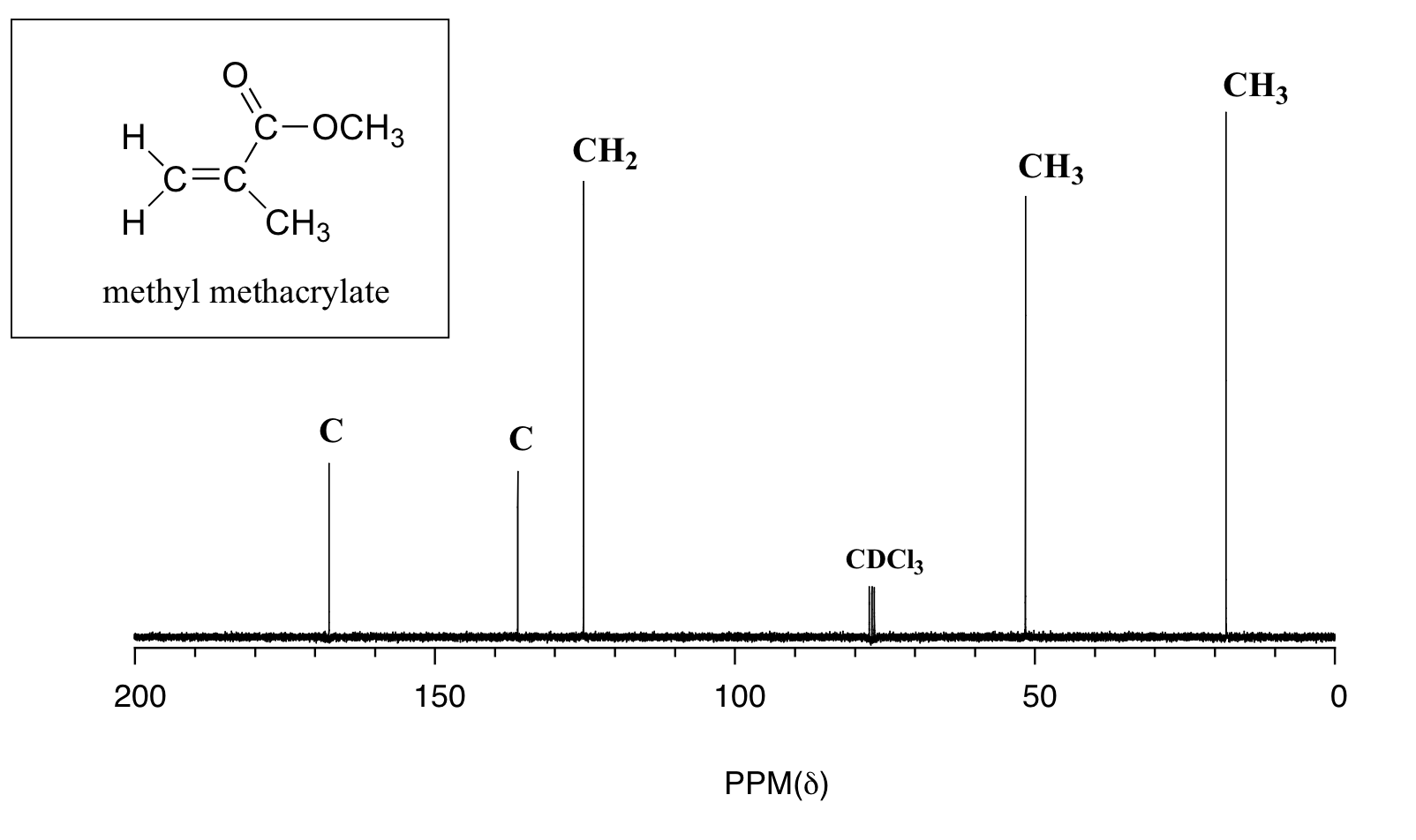
Carbon13 NMR Organic Chemistry Socratic

The carbonyl and methine region of 13C NMR spectra of various PCXCs

H NMR Table
(a) Trends in carbonyl reactivity. (b) Resonance stabilization. (c
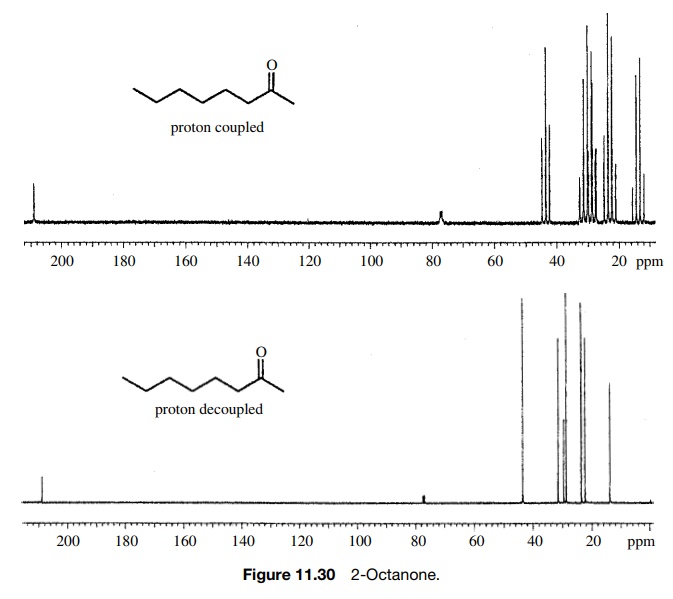
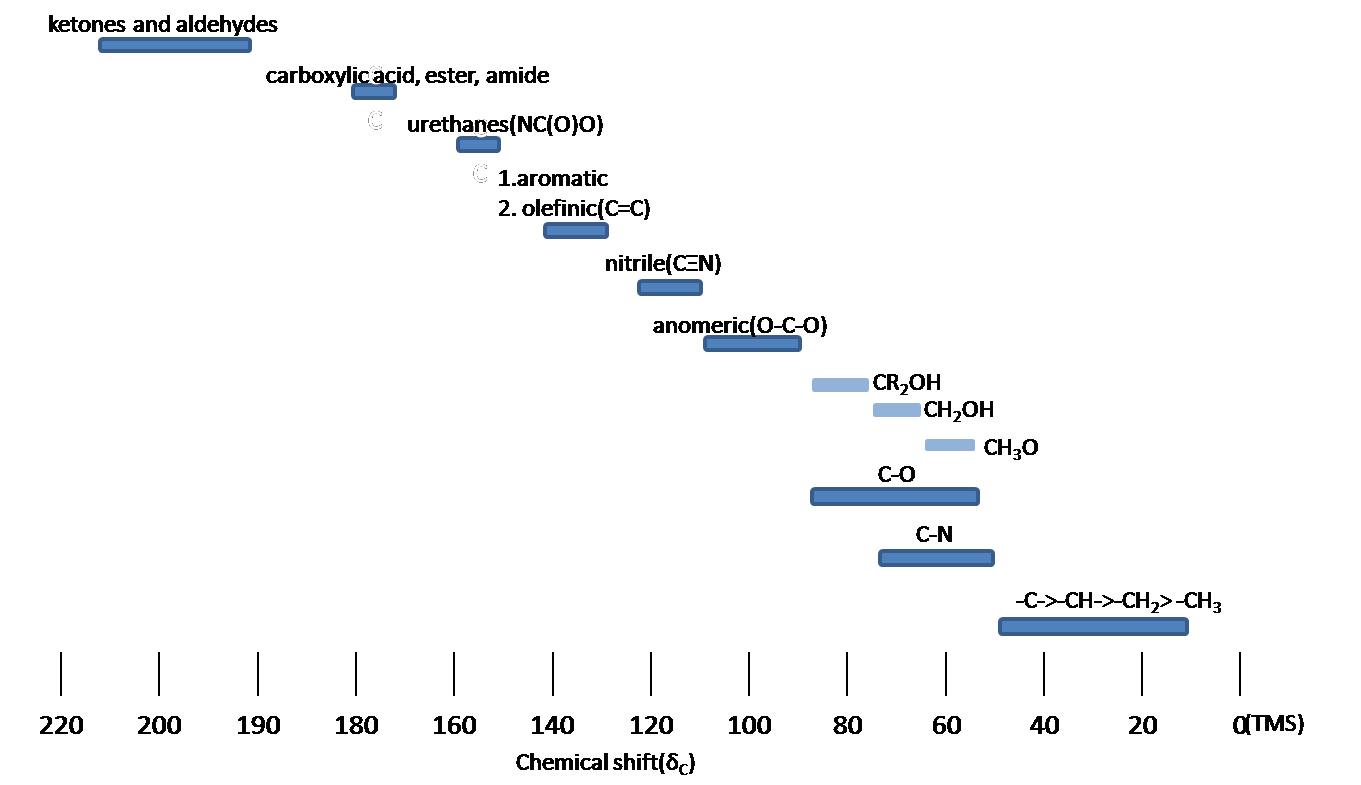
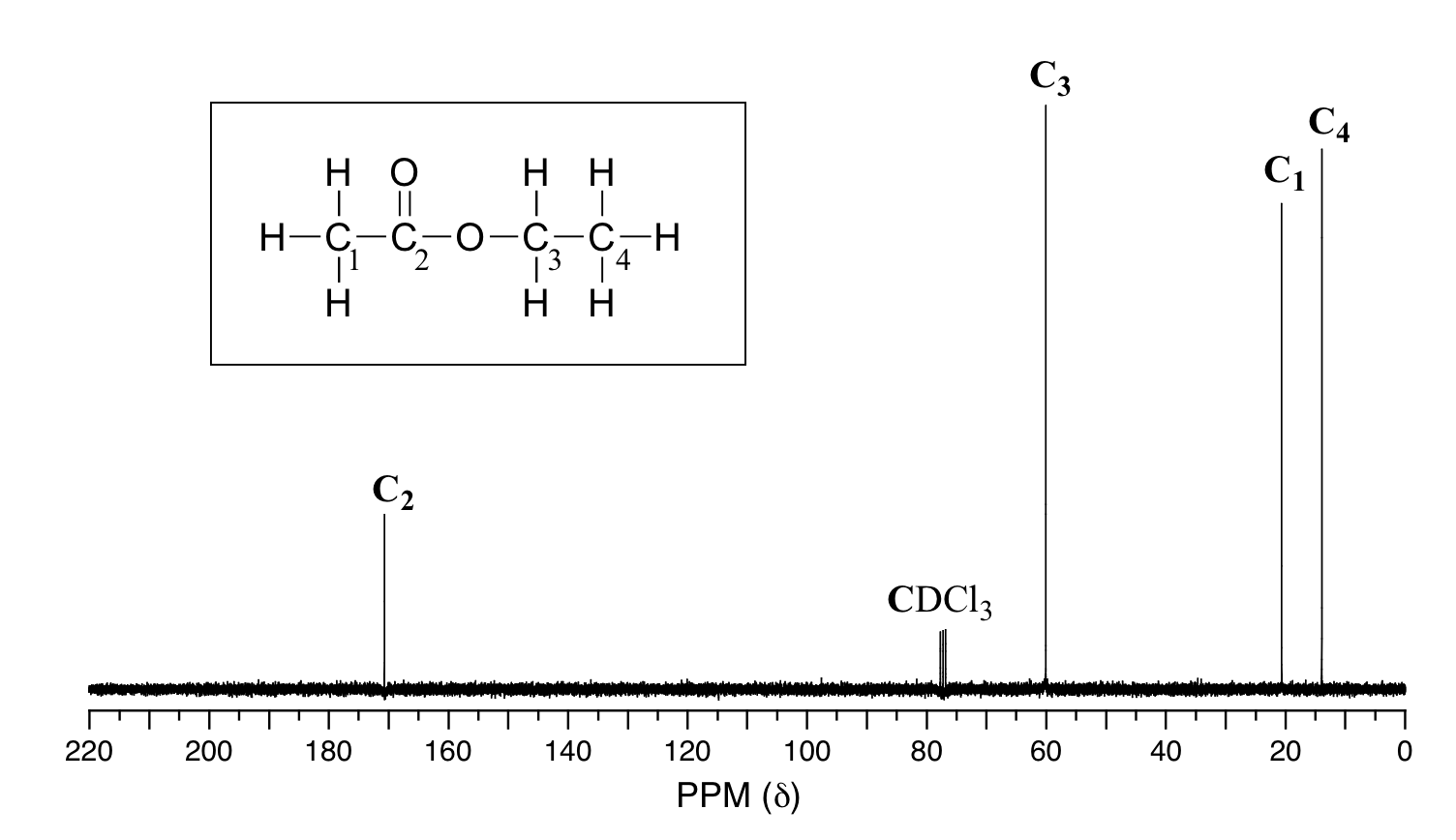
B18OA1 13 C NMR Spectroscopy 2 Typical chemical shifts 13 C NMR chemical shifts fall roughly into two regions, above and below 100 ppm: sp 2 carbons to the left, sp 3 to the right. • Aliphatic (sp 3-hybridised) carbons give rise to a signal in the 0 − 50 ppm region; substitution with an electronegative atom (O, N, Cl, F) can shift the signal downfield to about 80 ppm.. The 13 C NMR spectrum for 3-buten-2-one is: Using the table above, you can assign each peak to each carbon. The peak at just under 200 ppm is due to a carbon-oxygen double bond. The two peaks at 137 ppm and 129 ppm are due to the carbons at either end of the carbon-carbon double bond.




